
What Is a Forging Press? Exploring Metal Shaping Now
Did You Know? The automotive, aerospace, and heavy-duty machinery industries rely heavily on a single, powerful machine to shape robust, long-lasting metal parts—the forging press. But what exactly is a forging press, and how does it function? Whether you’re a seasoned manufacturing professional or simply intrigued by industrial machinery, this guide provides an in-depth look into What Is a Forging Press and the fascinating world of forging presses.

Introduction to Forging Presses
What is a Forging Press?
What Is a Forging Press? A forging press is specialized machinery built to shape and compress metal workpieces through the application of intense pressure. Unlike other metalworking techniques, such as cutting or milling (where material is removed), forging presses rely on compressive force to reshape metal into specified forms, producing components known for remarkable strength and durability. This powerful application of pressure makes forging presses indispensable in creating parts capable of withstanding extreme stress and wear over time.
A Brief History of Forging Presses
The history of forging presses dates back to ancient times, rooted in early metalworking practices. Traditionally, blacksmiths manually hammered metal to shape it through repeated strikes. The Industrial Revolution introduced mechanical hammers, gradually leading to today’s modern forging presses, equipped with hydraulic and mechanical systems that offer precise control over force and speed. This evolution has allowed forging presses to transform industries by providing the necessary power to create robust components with unparalleled accuracy.
Industrial Importance
Forging presses play a critical role across several industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. The use of forging presses allows manufacturers to create metal parts that not only demonstrate exceptional strength but also remain resilient against wear and fatigue, making them ideal for demanding environments. From automotive crankshafts to aircraft turbine disks, forging presses are essential to producing components that perform reliably across a wide spectrum of applications.
Types of Forging Presses
Mechanical Forging Presses
Mechanical forging presses generate force through a combination of flywheels and toggle mechanisms. Known for their rapid action, these presses are designed for high-speed production, capable of delivering quick, repetitive strikes that efficiently shape metal. Mechanical presses are typically found in high-volume production environments where speed and consistency are crucial.
Hydraulic Forging Presses
Hydraulic forging presses apply force using hydraulic systems, delivering a steady, controllable pressure. Unlike mechanical presses, which deliver short bursts of force, hydraulic presses maintain continuous pressure, making them well-suited for shaping larger or more complex parts. This steady force allows for precision, making hydraulic presses ideal for intricate designs and detailed metalwork.
Screw (or Friction) Presses
Screw presses, sometimes referred to as friction presses, apply force using a screw mechanism. Although these presses may not reach the speed of mechanical presses, they are highly valued for their precision. Screw presses are often chosen for producing smaller, detailed parts in applications that require exacting standards and meticulous control.
Servo Presses
Servo presses, a modern innovation in forging technology, operate through servomotors that offer precise, programmable control over force and speed, resulting in high accuracy and energy efficiency. Increasingly popular in advanced manufacturing environments, servo presses are used where both precision and energy savings are essential.
How a Forging Press Functions
Mechanics of Forging Presses
Forging presses work by exerting extreme pressure on metal within a die—a custom-shaped mold that defines the final form of the part. The press head, or ram, descends onto the metal workpiece, compressing it into the die shape. Critical factors such as pressure, die design, and temperature all contribute to determining the final product’s shape and properties, ensuring dimensional accuracy and desired structural characteristics.
Cold vs. Hot Forging
Forging processes are generally classified as either cold or hot forging. Cold forging takes place at room temperature, allowing for high precision and a smooth finish. However, it requires higher force and is often reserved for softer metals. Hot forging, by contrast, involves heating the metal to improve malleability. Though less precise, hot forging is ideal for tougher metals, resulting in parts with superior strength and resilience.
Forging Process Steps
Heating the Metal: For hot forging, metal is heated to an optimal temperature to make it more malleable for shaping.

Positioning in the Die: The heated workpiece is placed in the die, which forms the desired shape.
Applying Pressure: The forging press compresses the metal to fill the die’s contours.
Cooling: The forged part is cooled, solidifying its form and increasing its durability.
Key Applications of Forging Presses
Automotive Components
Forging presses are crucial in producing high-strength automotive components, including crankshafts, axles, and gears, which must endure continuous use and significant stress. The resilience provided by forging enhances component lifespan by reducing susceptibility to wear and damage.
Aerospace Parts
In aerospace, components must withstand extreme conditions, from high-stress loads to rapid temperature fluctuations. Forging presses produce critical parts such as turbine disks, engine components, and structural supports, ensuring these components meet stringent safety and performance standards.
Tool and Die Manufacturing
Forging presses are essential in the production of high-precision tools and dies used in other manufacturing processes. These tools must be durable and accurate, making forging presses invaluable in high-volume production environments where consistency is key.
Construction and Mining Equipment
Forging presses are also integral to producing components for construction and mining machinery, where resilience and durability are paramount. Components like drill bits, excavator arms, and crane hooks are typically forged to endure extreme forces and challenging environmental conditions.
Benefits and Limitations of Forging Presses
Strength and Durability
Components forged under the intense pressure of a forging press often exhibit greater strength and durability than parts produced by casting or machining. The compressive force refines the metal’s grain structure, resulting in a dense, uniform piece capable of handling high-stress applications and resisting wear over time.
Production Efficiency
Forging presses, especially mechanical ones, are efficient in high-volume manufacturing. Their capacity for rapid operation makes them ideal for applications requiring quick production cycles and large output.
Reduced Material Waste
Forging reshapes metal without significant material removal, unlike machining processes that cut away material. This approach minimizes waste, making it a more sustainable option, especially in large-scale manufacturing where material efficiency is essential.
Limitations
Despite their advantages, forging presses have some limitations. These machines require substantial investment and can be energy-intensive, especially hydraulic models. Additionally, precise temperature control is often needed to ensure quality, adding to the complexity of operations.
Innovations and Future Trends in Forging Press Technology
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are transforming forging processes by reducing human labor and enhancing precision. Automated systems offer consistency and repeatability, improving production efficiency and product quality in high-demand settings.
Environmentally Friendly Forging
With a growing focus on sustainability, recent innovations include electric-powered presses, which reduce emissions and operate more efficiently. Additionally, new processes are being developed to minimize waste and lessen the environmental impact of forging.
Advanced Materials
Forging presses are now able to work with advanced materials, such as high-strength alloys and composites, which expand the possibilities for producing lightweight yet strong components. In aerospace, where reducing weight is as crucial as maximizing durability, these materials are invaluable.
Digital Monitoring and AI
Modern forging presses increasingly use digital monitoring and AI for real-time quality control. These technologies allow operators to make adjustments based on live data, improving accuracy, reducing waste, and minimizing defects.
Forging Press Supplier: GUANGDUAN
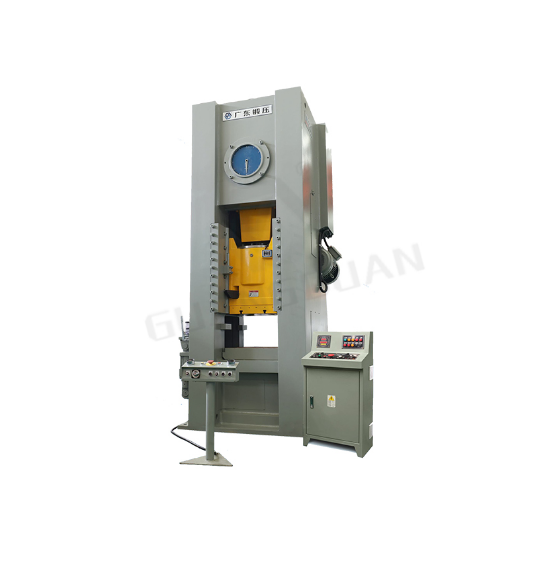
What Is a Forging Press? As a leading supplier, GUANGDUAN offers state-of-the-art forging press equipment for precision metal shaping. The JH31 Series Closed Type Single Point Forge Press Machine stands out as a robust option for industries requiring both precision and durability. Built with a monolithic box-type structure, the JH31 series provides high rigidity, while a strong crankshaft enhances its load-bearing capacity. The series also features a long-lasting wet-type clutch and a four-surface full-guideway system for improved guiding accuracy.

Key Features of the JH31 Series:
Digital Die Calibration Display: Facilitates quick and easy setup for efficient die calibration.
Hydraulic Overload Protection: Ensures safe operation under high pressure.
Automation Options: Offers photoelectric protection, automatic feeding, and uncoiling, making it ideal for high-efficiency production.
With applications across automotive, motorcycle, hardware, instrumentation, and other industries, the JH31 Series is versatile and widely applicable.
Conclusion
What Is a Forging Press? In conclusion, forging presses are powerful, essential tools in modern manufacturing. With their ability to deliver strength, precision, and efficiency, and with suppliers like GUANGDUAN at the forefront of technological advancement, the future of forging press technology is full of potential for even greater innovations and improved sustainability.
CONTACT US

Guangdong Metal Forming Machine Works Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us



