
Hydraulic Press for Forging: Fit Your Requirements
Forging is an ancient art that dates back to the times when humans began manipulating metals. In early civilizations, blacksmiths used simple tools like hammers and anvils to shape metals into desired forms. This process not only allowed the production of weapons, tools, and jewelry, but it also laid the foundation for the advancement of technology and civilization. The Bronze Age, Iron Age, and subsequent periods witnessed the evolution of forging techniques and tools.
Hydraulic Press for Forging: Basics of Hydraulic Presses
1. Hydraulic Press for Forging: The Science Behind Hydraulics
Hydraulics is a branch of science that deals with the mechanical properties and use of fluids. In the context of hydraulic presses, the principle is simple yet effective: when a force is applied to a fluid in a confined space, the fluid transmits that force in all directions, thereby amplifying it. This phenomenon allows a relatively small force, applied over a large area, to be transformed into a larger force over a smaller area.
2. Core Components of a Hydraulic Press: Pump, Cylinder, and Working Fluid
At the heart of any Hydraulic Press for Forging are its core components. GUANGDUAN, as a leading manufacturer, ensures that these components are of top quality.
Pump: This is responsible for pressurizing the working fluid, allowing it to transmit power.
Cylinder: The pressurized fluid from the pump acts on a piston within the cylinder. As the fluid pushes the piston, the piston exerts force on the metal piece being forged.
Working Fluid: Often an oil, the working fluid is incompressible, which means it can efficiently transmit the force from the pump to the cylinder.
3. Hydraulic Press for Forging: Importance of Forging in Modern Manufacturing
In today’s manufacturing industry, forging is indispensable. It provides components with enhanced structural strength, precision, and durability. Modern aircraft, automobiles, infrastructure, and countless other industries rely heavily on forged parts. Their consistency, reliability, and toughness are unparalleled, making forging an essential process in modern-day production lines.
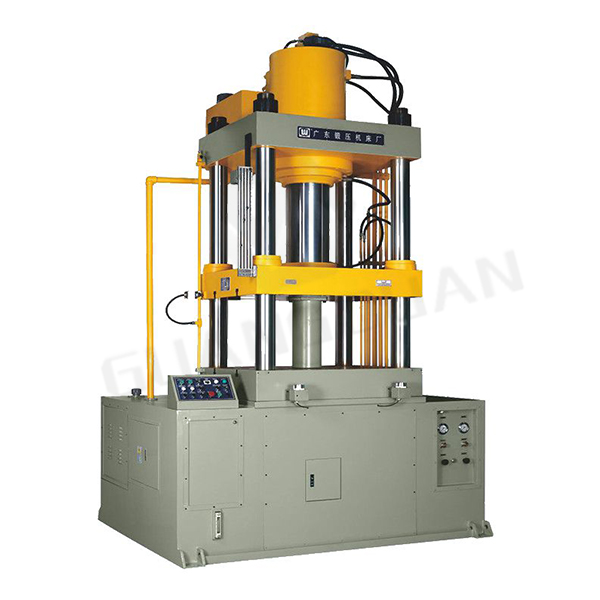

Hydraulic Press for Forging: The Hydraulic Press Forging Process
1. Material Preparation: Heating, Selection, and Preconditioning
Before forging can commence, materials must be readied. This involves the selection of the appropriate metal or alloy, which is subsequently heated to the desired temperature. This temperature varies depending on the material and the specific forging process. Preconditioning might also include treating the material to ensure its structural integrity during the forging.
2. Mold and Die Design: Importance of Precise Tooling
Central to the forging process is the design of molds and dies. These tools, often constructed from hard metals, are crafted with precision. This exactness ensures that the final forged product meets the necessary specifications and dimensions. It’s crucial to invest in high-quality tooling to avoid inaccuracies in the forged product.
3. Forging Cycle: Loading, Pressing, and Unloading
Once materials are prepared and tools are in place, the forging cycle begins. The process starts with loading the heated material into the press. The hydraulic press, powered by immense pressure from hydraulic fluids, then applies force onto the material, causing it to take the shape of the mold or die. After the pressing, the forged material is unloaded, marking the completion of one forging cycle.
4. Post-forging Processes: Trimming, Heat Treatment, and Finishing
After forging, the product usually undergoes several additional processes. Trimming is done to remove any excess material. Heat treatment can alter the structural properties of the material, improving its durability or strength. Lastly, finishing processes give the forged product its final appearance and texture, ensuring it’s ready for its intended use.
Hydraulic Press for Forging: Types of Forging Achievable with Hydraulic Presses
1. Open-Die Forging: Basic Shaping and Elongation
This method employs basic shaping techniques, making it suitable for larger pieces where the finish doesn’t require high precision. Open-die forging is often utilized when elongating a workpiece or producing simple shapes.
2. Closed-Die Forging: High Precision Products with Detailed Features
Contrary to open-die forging, closed-die forging relies on pre-made molds. These molds produce products with intricate designs and close tolerances, resulting in high-precision components suitable for specific applications.
3. Coining: Producing Intricate Details on a Workpiece’s Surface
Coining is a forging process that impresses detailed designs onto a workpiece’s surface. This process is essential in industries like minting where fine, consistent details on products are paramount.
4. Upset Forging: Increasing the Diameter of a Work Section
Upset forging focuses on the diameter of a section of the workpiece. By applying force, it can increase the diameter, creating a larger cross-sectional area at specific points.
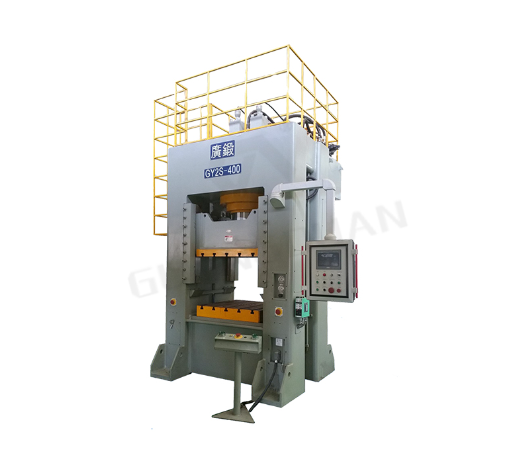

Hydraulic Press for Forging: Traditional Forging vs. Hydraulic Press Forging
1. Overview of Manual Hammer and Anvil Methods
Traditional forging primarily involved manual labor. Blacksmiths would use hammers to strike metal pieces placed on anvils, shaping them with skill and precision. This method, although time-consuming, was effective in producing individualized pieces and bespoke creations. The human touch, the rhythm of the hammer, and the glow of heated metal were quintessential to this traditional craft.
2. Transition to Powered Hammer and Press Methods
As industries grew and the demand for mass production increased, the need for faster and more consistent forging methods became apparent. Enter powered hammers and press methods. These innovations allowed for quicker, more consistent, and larger-scale production of forged components. Among the modern methods, Hydraulic Press for Forging, especially from manufacturers like GUANGDUAN, has become particularly significant in recent years.
Hydraulic Press for Forging: Case Studies
1. Hydraulic Press for Forging: Real-world Examples of Products Made with Hydraulic Press Forging
Hydraulic press forging has been instrumental in manufacturing numerous everyday products. From automotive parts to construction materials, the versatility of hydraulic presses is evident in the varied items they produce.
2. Hydraulic Press for Forging: Testimonies from Industry Leaders and Their Experiences
Industry veterans vouch for the efficacy and precision of hydraulic press forging. One such testimony is from the esteemed hydraulic press for forging machine manufacturer, GUANGDUAN. They stand by the efficiency of their machines, which have catered to diverse industries, showcasing the versatility and reliability of hydraulic press forging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hydraulic Press for Forging has revolutionized the art of shaping metals, combining age-old principles with modern-day technology. Manufacturers like GUANGDUAN play an integral role in pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, ensuring that forging remains a vital and efficient process in modern manufacturing.
CONTACT US

Guangdong Metal Forming Machine Works Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us



