
What is Closed-Die Forging? A Look into Forging Press Machinery Techniques
Have the intricacies ever been considered by you regarding how robust and precisely shaped metal components, essential to vehicles like cars and motorcycles, or even more common items such as tools, are brought into existence? A significant portion of the answer can be found in a manufacturing technique that, while ancient, remains remarkably effective even in today’s advanced industrial landscape—a process known as closed-die forging. But how is this method, exactly, carried out? Which characteristics specifically contribute to its effectiveness when manufacturing a wide array of products? Moreover, in what ways does modern machinery, particularly advanced models like the JH31 series Forging Press Machinery, serve to enhance this traditional forging technique? These fundamental questions are explored in the following sections, providing a thorough look at the forging process, the machinery involved, and the wide-ranging industrial applications it supports.

Understanding Closed-Die Forging
What is Closed-Die Forging?
Closed-die forging, also referred to as impression-die forging, is recognized as a sophisticated metal-shaping process wherein a workpiece is inserted between two dies, which function as precisely engineered metal molds, and significant force is exerted upon the metal, compelling it to conform to the contours of the die cavity. As a result of this high-pressure process, a metal component is created that not only possesses exceptional precision but also displays superior mechanical properties. The term “closed-die” arises from the fact that during the forging operation, the metal remains entirely enclosed within the die cavity, thereby ensuring a remarkably high level of dimensional accuracy and material integrity.
Why is Closed-Die Forging So Effective?
The remarkable effectiveness associated with the closed-die forging process largely originates from its capacity to generate extremely strong and durable components by subjecting the metal to extreme pressure. As this pressure is applied, the metal undergoes a transformation through plastic deformation, which significantly enhances its internal structure. The process compresses the metal, thereby increasing its density and refining its grain structure, resulting in the imparting of superior mechanical properties to the forged part, particularly when compared to other methods such as casting or machining. Consequently, closed-die forging proves especially well-suited for manufacturing components that are required to endure substantial mechanical stresses, such as crankshafts, gears, and connecting rods, all of which are crucial to the proper functioning of machinery and engines.
Common Applications of Closed-Die Forging
Closed-die forging has found widespread use in industries where strength, durability, and precision are critical. Major sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and energy production depend extensively on forged components, given the inherent strength and reliability these parts offer. In this process, components essential to motorcycles, airplanes, and gas appliances are produced—items that must meet strict standards for accuracy and be capable of enduring harsh conditions, all to ensure the safety and performance of these sophisticated systems.
The Role of Forging Press Machinery in Closed-Die Forging
Overview of Forge Press Machines
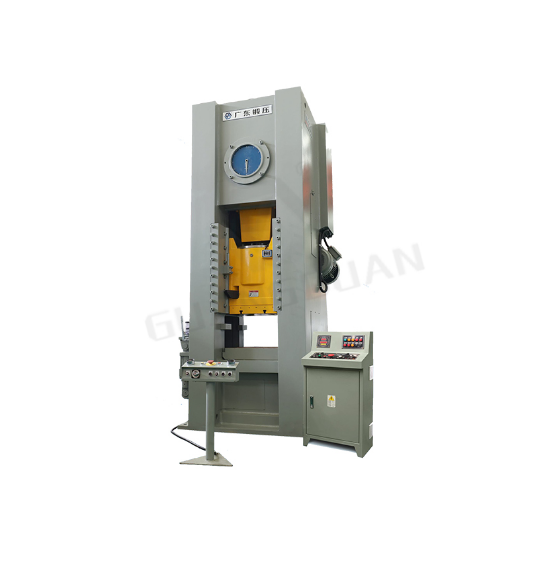
Central to the entire closed-die forging process is the forge press machine, which functions as the primary tool responsible for delivering the immense forces required to reshape the metal into its final form. Designed specifically to apply tremendous pressure, forge press machines ensure that the metal is compressed into every contour of the die cavity, resulting in a component that precisely matches the desired specifications. These machines come in various sizes and configurations, tailored to meet the specific demands of different materials and applications. A prime example of modern forge press technology is the JH31 series narrow-table closed-type single-point forge press, manufactured by GUANGDUAN, which incorporates advanced features to improve performance and durability.

Key Features of the JH31 Series Forging Press Machinery
The JH31 series forge press has been meticulously engineered to satisfy the demanding requirements of modern industrial forging operations. Its body, constructed using a high-strength monolithic box-type structure, provides exceptional rigidity, enabling it to withstand the enormous forces that are routinely applied during forging. Additionally, some models within the series include a four-pull level pre-light structure, which enhances the overall strength and stability of the machine.
A distinguishing feature of the JH31 series is its incorporation of an eccentric shaft crankshaft, which offers a robust bearing capacity, ensuring that the machine can operate smoothly, even under heavy loads. Additionally, the inclusion of a wet-type clutch extends the machine’s operational life by reducing maintenance needs. Moreover, the machine’s four-surface full-guideway slide block significantly improves guiding precision, effectively minimizing deviations and errors during the forging process, thereby guaranteeing that each component meets the highest quality standards.
Advanced Functionality for Precision and Safety
The integration of advanced technological features into the JH31 Forging Press Machinery series sets it apart from many other forge press machines, particularly in terms of precision and ease of use. The machine is equipped with a digitally-displayed die set height adjustment mechanism, enabling rapid and highly accurate calibration of the tooling. This functionality greatly simplifies the setup process and reduces the likelihood of errors occurring during production.
In terms of safety, the larger models within the JH31 series, such as the JH31-400/630/800, come with a hydraulic overload protection system designed to prevent damage to both the machine and the forged components in the event of an unexpected overload. Additionally, the smaller models, such as the JH31-200/300, utilize a wedge-shaped iron die unlocking device, ensuring safe and secure operation throughout the forging process.
Applications of the JH31 Series Forging Press Machinery
Automotive Industry
Within the automotive sector, the JH31 series forge press machines play a pivotal role in producing critical components such as crankshafts, gears, and axles. These parts are subjected to substantial forces during vehicle operation and must therefore possess exceptional strength and durability. By leveraging the advanced precision and power offered by the JH31 series, automotive manufacturers can consistently produce parts that meet the stringent quality standards demanded by the industry, contributing both to the performance and safety of modern vehicles.
Motorcycles and Daily Hardware
In the field of motorcycle manufacturing, the strength and precision provided by the JH31 series forge press machines are indispensable for the production of key components such as connecting rods, engine parts, and forks. The machine’s ability to produce large quantities of forged parts with minimal variation makes it particularly well-suited for this application. Additionally, the JH31 series is utilized in the production of daily hardware items, such as tools and kitchenware, where consistency and durability are highly valued.
Gas Appliances and Instrumentation
The JH31 series forge press is also widely employed in industries that require components capable of withstanding high pressures and extreme temperatures, such as the gas appliance and instrumentation sectors. The precise and reliable nature of the forged parts produced by these machines ensures that gas appliances, often operating under challenging conditions, remain safe and efficient throughout their service life.
Automation and Safety in Modern Forge Press Machinery
Automated Production for Increased Efficiency
As the demand for high-volume production continues to grow, industries are increasingly turning to automation to meet these requirements. The JH31 series can be equipped with features such as automatic feeding devices and uncoiling leveling systems, allowing the machine to operate with minimal human intervention. This move toward automation not only enhances the consistency of the products being forged but also significantly boosts production speed and reduces labor costs, making it an ideal choice for industries involved in large-scale manufacturing.
Safety Features for Operator Protection
Given the immense forces involved in the forging process, ensuring operator safety is a top priority in the design of forge press machines. The JH31 series is equipped with photo-electric protection systems that automatically stop the machine if an object, such as a human hand, enters the working area. These safety systems, combined with the hydraulic overload system, ensure that the JH31 series operates in a safe and secure environment without compromising on performance.
Conclusion: The Power of Closed-Die Forging and Modern Machinery
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, closed-die forging remains one of the most efficient methods for producing metal components with exceptional strength and precision. With advancements in forge press machinery, like those seen in the JH31 series from GUANGDUAN, industries are able to benefit from increased efficiency, safety, and accuracy. Whether used in automotive manufacturing, gas appliance production, or daily hardware creation, the combination of traditional forging techniques with cutting-edge machinery ensures that closed-die forging will continue to play a pivotal role in modern industry for years to come.
CONTACT US

Guangdong Metal Forming Machine Works Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us



